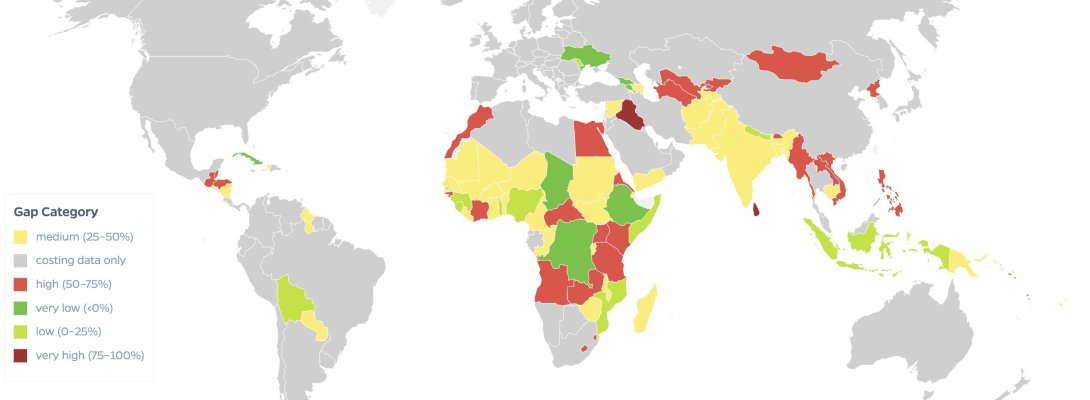
The immunization program costing data presented in VIEW-hub were estimated using the WHO coverage forecast for Immunization Agenda 2030 (IA2030), among 14 pathogens: Hepatitis B (Hep B), Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), Human papillomavirus (HPV), Japanese encephalitis (JE), Measles, Meningitis A (Men A), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Rotavirus, Rubella, Yellow Fever (YF), Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, and Tuberculosis. This forecast includes routine vaccine costs, routine delivery costs, and non-routine costs (Supplementary Immunization Activities (SIA) and stockpile). Immunization financing data comprises government expenditure, Gavi funding, out-of-pocket costs, prepaid private spending, and additional development assistance for health (DAH). Funding gap data represent the disparity between the immunization costs and the level of immunization financing. Identifying the narrowing gap, recognizing the growing gap and determining the additional level of investment needed are essential for policy development such as resource mobilization and sustainable financial strategies to achieve the goal of IA2030.
All estimates presented in VIEW-hub below are during the period 2021-2030 among 94 low- and middle-income countries.
Please interpret the cost estimates with caution. The IA2030 impact coverage is based on 2019 estimates, without taking into account disruptions during the pandemic.